Combinatorics (Fall 2010)/Partitions, sieve methods
Partitions
We count the ways of partitioning [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] identical objects into [math]\displaystyle{ k }[/math] unordered groups. This is the problem of counting the ways partitioning a number [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] into [math]\displaystyle{ k }[/math] unordered parts.
A [math]\displaystyle{ k }[/math]-partition of a number [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] is a multiset [math]\displaystyle{ \{x_1,x_2,\ldots,x_k\} }[/math] with [math]\displaystyle{ x_i\ge 1 }[/math] for every element [math]\displaystyle{ x_i }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ x_1+x_2+\cdots+x_k=n }[/math].
We define [math]\displaystyle{ p_k(n) }[/math] as the number of [math]\displaystyle{ k }[/math]-partitions of [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math].
For example, number 7 has the following partitions:
Equivalently, we can also define that A [math]\displaystyle{ k }[/math]-partition of a number [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] is a [math]\displaystyle{ k }[/math]-tuple [math]\displaystyle{ (x_1,x_2,\ldots,x_k) }[/math] with:
- [math]\displaystyle{ x_1\ge x_2\ge\cdots\ge x_k\ge 1 }[/math];
- [math]\displaystyle{ x_1+x_2+\cdots+x_k=n }[/math].
[math]\displaystyle{ p_k(n) }[/math] the number of integral solutions to the above system.
Let [math]\displaystyle{ p(n)=\sum_{k=1}^n p_k(n) }[/math] be the total number of partitions of [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math]. The function [math]\displaystyle{ p(n) }[/math] is called the partition number.
Proposition - [math]\displaystyle{ p_k(n)=\sum_{j=1}^kp_j(n-k) }[/math].
Theorem For any fixed [math]\displaystyle{ k }[/math],
- [math]\displaystyle{ p_k(n)\sim\frac{n^{k-1}}{k!(k-1)!} }[/math],
as [math]\displaystyle{ n\rightarrow \infty }[/math].
Ferrers diagram
Young tableaux
Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion
Let [math]\displaystyle{ A }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ B }[/math] be two finite sets. The cardinality of their union is
- [math]\displaystyle{ |A\cup B|=|A|+|B|-{\color{Blue}|A\cap B|} }[/math].
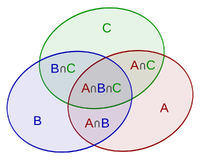
For three sets [math]\displaystyle{ A }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ B }[/math], and [math]\displaystyle{ C }[/math], the cardinality of the union of these three sets is computed as
- [math]\displaystyle{ |A\cup B\cup C|=|A|+|B|+|C|-{\color{Blue}|A\cap B|}-{\color{Blue}|A\cap C|}-{\color{Blue}|B\cap C|}+{\color{Red}|A\cap B\cap C|} }[/math].
This is illustrated by the following figure.
Generally, the Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion states the rule for computing the union of [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] finite sets [math]\displaystyle{ A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_n }[/math], such that
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \left|\bigcup_{i=1}^nA_i\right| &= \sum_{I\subseteq\{1,\ldots,n\}}(-1)^{|I|-1}\left|\bigcap_{i\in I}A_i\right|. \end{align} }[/math]
In combinatorial enumeration, the Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion is usually applied in its complement form.
Let [math]\displaystyle{ A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_n\subseteq U }[/math] be subsets of some finite set [math]\displaystyle{ U }[/math]. Here [math]\displaystyle{ U }[/math] is some universe of combinatorial objects, whose cardinality is easy to calculate (e.g. all strings, tuples, permutations), and each [math]\displaystyle{ A_i }[/math] contains the objects with some specific property (e.g. a "pattern") which we want to avoid. The problem is to count the number of objects without any of the [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] properties. We write [math]\displaystyle{ \bar{A_i}=U-A }[/math]. The number of objects without any of the properties [math]\displaystyle{ A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_n }[/math] is
[math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} \left|\bar{A_1}\cap\bar{A_2}\cap\cdots\cap\bar{A_n}\right|=\left|U-\bigcup_{i=1}^nA_i\right| &= |U|-\sum_{I\subseteq\{1,\ldots,n\}}(-1)^{|I|}\left|\bigcap_{i\in I}A_i\right|. \end{align} }[/math]
For an [math]\displaystyle{ I\subseteq\{1,2,\ldots,n\} }[/math], we denote
- [math]\displaystyle{ A_I=\bigcap_{i\in I}A_i }[/math]
with the convention that [math]\displaystyle{ A_\emptyset=U }[/math]. The above equation is stated as:
Principle of Inclusion-Exclusion - Let [math]\displaystyle{ A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_n }[/math] be a family of subsets of [math]\displaystyle{ U }[/math]. Then the number of elements of [math]\displaystyle{ U }[/math] which lie in none of the subsets [math]\displaystyle{ A_i }[/math] is
- [math]\displaystyle{ \sum_{I\subseteq\{1,\ldots, n\}}(-1)^{|I|}|A_I| }[/math].
- Let [math]\displaystyle{ A_1,A_2,\ldots,A_n }[/math] be a family of subsets of [math]\displaystyle{ U }[/math]. Then the number of elements of [math]\displaystyle{ U }[/math] which lie in none of the subsets [math]\displaystyle{ A_i }[/math] is
Let [math]\displaystyle{ S_k=\sum_{|I|=k}|A_I|\, }[/math]. Conventionally, [math]\displaystyle{ S_0=|A_\emptyset|=|U| }[/math]. The principle of inclusion-exclusion can be expressed as
Surjections
In the twelvefold way, we discuss the counting problems incurred by the mappings [math]\displaystyle{ f:N\rightarrow M }[/math]. The basic case is that elements from both [math]\displaystyle{ N }[/math] and [math]\displaystyle{ M }[/math] are distinguishable. In this case, it is easy to count the number of arbitrary mappings (which is [math]\displaystyle{ m^n }[/math]) and the number of injective (one-to-one) mappings (which is [math]\displaystyle{ (m)_n }[/math]), but the number of surjective is difficult. Here we apply the principle of inclusion-exclusion to count the number of surjective (onto) mappings.
Theorem - The number of surjective mappings from an [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math]-set to an [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math]-set is given by
- [math]\displaystyle{ \sum_{k=1}^m(-1)^{m-k}{m\choose k}k^n }[/math].
- The number of surjective mappings from an [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math]-set to an [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math]-set is given by
Proof. Let [math]\displaystyle{ U=\{f:[n]\rightarrow[m]\} }[/math] be the set of mappings from [math]\displaystyle{ [n] }[/math] to [math]\displaystyle{ [m] }[/math]. Then [math]\displaystyle{ |U|=m^n }[/math].
For [math]\displaystyle{ i\in[m] }[/math], let [math]\displaystyle{ A_i }[/math] be the set of mappings [math]\displaystyle{ f:[n]\rightarrow[m] }[/math] that none of [math]\displaystyle{ j\in[n] }[/math] is mapped to [math]\displaystyle{ i }[/math], i.e. [math]\displaystyle{ A_i=\{f:[n]\rightarrow[m]\setminus\{i\}\} }[/math], thus [math]\displaystyle{ |A_i|=(m-1)^n }[/math].
More generally, for [math]\displaystyle{ I\subseteq [m] }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ A_I=\bigcap_{i\in I}A_i }[/math] contains the mappings [math]\displaystyle{ f:[n]\rightarrow[m]\setminus I }[/math]. And [math]\displaystyle{ |A_I|=(m-|I|)^n\, }[/math].
A mapping [math]\displaystyle{ f:[n]\rightarrow[m] }[/math] is surjective if [math]\displaystyle{ f }[/math] lies in none of [math]\displaystyle{ A_i }[/math]. By the principle of inclusion-exclusion, the number of surjective [math]\displaystyle{ f:[n]\rightarrow[m] }[/math] is
- [math]\displaystyle{ \sum_{\subseteq[m]}(-1)^{|I|}\left|A_I\right|=\sum_{I\subseteq[m]}(-1)^{|I|}(m-|I|)^n=\sum_{j=0}^m(-1)^j{m\choose j}(m-j)^n }[/math].
Let [math]\displaystyle{ k=m-j }[/math]. The theorem is proved.
- [math]\displaystyle{ \square }[/math]
Recall that, in the twelvefold way, we establish a relation between surjections and partitions.
- Surjection to ordered partition:
- For a surjective [math]\displaystyle{ f:[n]\rightarrow[m] }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ (f^{-1}(0),f^{-1}(1),\ldots,f^{-1}(m-1)) }[/math] is an ordered partition of [math]\displaystyle{ [n] }[/math].
- Ordered partition to surjection:
- For an ordered [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math]-partition [math]\displaystyle{ (B_0,B_1,\ldots, B_{m-1}) }[/math] of [math]\displaystyle{ [n] }[/math], we can define a function [math]\displaystyle{ f:[n]\rightarrow[m] }[/math] by letting [math]\displaystyle{ f(i)=j }[/math] if and only if [math]\displaystyle{ i\in B_j }[/math]. [math]\displaystyle{ f }[/math] is surjective since as a partition, none of [math]\displaystyle{ B_i }[/math] is empty.
Therefore, we have a one-to-one correspondence between surjective mappings from an [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math]-set to an [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math]-set and the ordered [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math]-partitions of an [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math]-set.
The Stirling number of the second kind [math]\displaystyle{ S(n,m) }[/math] is the number of [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math]-partitions of an [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math]-set. There are [math]\displaystyle{ m! }[/math] ways to order an [math]\displaystyle{ m }[/math]-partition, thus the number of surjective mappings [math]\displaystyle{ f:[n]\rightarrow[m] }[/math] is [math]\displaystyle{ m! S(n,m) }[/math]. Combining with what we have proved for surjections, we give the following result for the Stirling number of the second kind.
Proposition - [math]\displaystyle{ S(n,m)=\frac{1}{m!}\sum_{k=1}^m(-1)^{m-k}{m\choose k}k^n }[/math].
Derangements
We now count the number of bijections from a set to itself with no fixed points. This is the derangement problem.
For a permutation [math]\displaystyle{ \pi }[/math] of [math]\displaystyle{ \{1,2,\ldots,n\} }[/math], a fixed point is such an [math]\displaystyle{ i\in\{1,2,\ldots,n\} }[/math] that [math]\displaystyle{ \pi(i)=i }[/math]. A derangement of [math]\displaystyle{ \{1,2,\ldots,n\} }[/math] is a permutation of [math]\displaystyle{ \{1,2,\ldots,n\} }[/math] that has no fixed points.
Theorem - The number of derangements of [math]\displaystyle{ \{1,2,\ldots,n\} }[/math] given by
- [math]\displaystyle{ n!\sum_{k=0}^n\frac{(-1)^k}{k!}\approx \frac{n!}{\mathrm{e}} }[/math].
- The number of derangements of [math]\displaystyle{ \{1,2,\ldots,n\} }[/math] given by
Proof. Let [math]\displaystyle{ U }[/math] be the set of all permutations of [math]\displaystyle{ \{1,2,\ldots,n\} }[/math]. So [math]\displaystyle{ |U|=n! }[/math].
Let [math]\displaystyle{ A_i }[/math] be the set of permutations with fixed point [math]\displaystyle{ i }[/math]; so [math]\displaystyle{ |A_i|=(n-1)! }[/math]. More generally, for any [math]\displaystyle{ I\subseteq \{1,2,\ldots,n\} }[/math], [math]\displaystyle{ A_I=\bigcup_{i\in I}A_i }[/math], and [math]\displaystyle{ |A_I|=(n-|I|)! }[/math], since permutations in [math]\displaystyle{ A_I }[/math] fix every point in [math]\displaystyle{ I }[/math] and permute the remaining points arbitrarily. A permutation is a derangement if and only if it lies in none of the sets [math]\displaystyle{ A_i }[/math]. So the number of derangements is
- [math]\displaystyle{ \sum_{I\subseteq\{1,2,\ldots,n\}}(-1)^{|I|}(n-|I|)!=\sum_{k=0}^n(-1)^k{n\choose k}(n-k)!=n!\sum_{k=0}^n\frac{(-1)^k}{k!}. }[/math]
By Taylor's series,
- [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{\mathrm{e}}=\sum_{k=0}^\infty\frac{(-1)^k}{k!}=\sum_{k=0}^n\frac{(-1)^k}{k!}\pm o\left(\frac{1}{n!}\right) }[/math].
It is not hard to see that [math]\displaystyle{ n!\sum_{k=0}^n\frac{(-1)^k}{k!} }[/math] is the closest integer to [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{n!}{\mathrm{e}} }[/math].
- [math]\displaystyle{ \square }[/math]
Therefore, there are about [math]\displaystyle{ \frac{1}{\mathrm{e}} }[/math] fraction of all permutations with no fixed points.
Permutations with restricted positions
We introduce a general theory of counting permutations with restricted positions. In the derangement problem, we count the number of permutations that [math]\displaystyle{ \pi(i)\neq i }[/math]. We now generalize to the problem of counting permutations which avoid a set of arbitrarily specified positions.
It is traditionally described using terminology from the game of chess. Let [math]\displaystyle{ B\subseteq \{1,\ldots,n\}\times \{1,\ldots,n\} }[/math], called a board. As illustrated below, we can think of [math]\displaystyle{ B }[/math] as a chess board, with the positions in [math]\displaystyle{ B }[/math] marked by "[math]\displaystyle{ \times }[/math]".
For a permutation [math]\displaystyle{ \pi }[/math] of [math]\displaystyle{ \{1,\ldots,n\} }[/math], define the graph [math]\displaystyle{ G_\pi(V,E) }[/math] as
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} G_\pi &= \{(i,\pi(i))\mid i\in \{1,2,\ldots,n\}\}. \end{align} }[/math]
This can also be viewed as a set of marked positions on a chess board. Each row and each column has only one marked position, because [math]\displaystyle{ \pi }[/math] is a permutation. Thus, we can identify each [math]\displaystyle{ G_\pi }[/math] as a placement of [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] rooks (“城堡”,规则同中国象棋里的“车”) without attacking each other.
For example, the following is the [math]\displaystyle{ G_\pi }[/math] of such [math]\displaystyle{ \pi }[/math] that [math]\displaystyle{ \pi(i)=i }[/math].
Now define
- [math]\displaystyle{ \begin{align} N_0 &= \left|\left\{\pi\mid B\cap G_\pi=\emptyset\right\}\right|\\ r_k &= \left|\left\{S\in{B\choose k} \,\bigg|\, \mbox{no two elements of }S\mbox{ have a common coordinate} \right\}\right| \end{align} }[/math]
Interpreted in chess game,
- [math]\displaystyle{ B }[/math]: a set of marked positions in an [math]\displaystyle{ [n]\times [n] }[/math] chess board.
- [math]\displaystyle{ N_0 }[/math]: the number of ways of placing [math]\displaystyle{ n }[/math] non-attacking rooks on the chess board such that none of these rooks lie in [math]\displaystyle{ B }[/math].
- [math]\displaystyle{ r_k }[/math]: number of ways of placing [math]\displaystyle{ k }[/math] non-attacking rooks on [math]\displaystyle{ B }[/math].
Our goal is to count [math]\displaystyle{ N_0 }[/math] in terms of [math]\displaystyle{ r_k }[/math]. This gives the number of permutations avoid all positions in a [math]\displaystyle{ B }[/math].
Theorem - [math]\displaystyle{ N_0=\sum_{k=0}^n(-1)^kr_k(n-k)! }[/math].
- Derangement problem
- Problème des ménages